
The Australian healthcare industry holds a sacred trust: safeguarding the highly sensitive personal information of its patients. This data, encompassing medical history, diagnoses, and treatment details, is fundamental to delivering quality care. However, the digital age has introduced a concerning reality – patient data is increasingly under siege from cyberattacks.
A 2023 report by the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) revealed a 78% increase in cyberattacks targeting healthcare organizations across the country. These attacks often target unauthorized access to sensitive data, with potentially devastating consequences. In 2022, a major Australian hospital system suffered a data breach that compromised the personal information of over 9 million patients, highlighting the vulnerability of healthcare data and the potential for large-scale disruption.
To combat these growing threats, Australian healthcare providers require robust security measures. Identity and Access Management (IAM) serves as a crucial line of defense. IAM governs who can access patient data, what information they can access, and for what purpose. By implementing a comprehensive IAM system, healthcare organizations can significantly strengthen their data security posture and minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
This guide is designed to empower Australian healthcare providers with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the world of IAM assessments. We will delve into the legalities surrounding patient data security, explore the benefits of IAM assessments, and outline the steps involved in conducting a thorough evaluation. By understanding and implementing effective IAM practices, Australian healthcare providers can ensure the continued privacy and security of their patients’ sensitive data.
Understanding Patient Data Security in Australia

Australian healthcare providers are entrusted with a significant responsibility: upholding the privacy and security of their patients’ highly sensitive data. This obligation is not only ethical but also enshrined in Australian law. The Privacy Act 1988 (Cth) serves as the cornerstone of data protection, outlining a set of mandatory Australian Privacy Principles (APPs) that all healthcare organizations must adhere to. These principles, administered by the Office of the Australian Information Commissioner (OAIC), govern the collection, use, disclosure, and storage of personal information, including patient data.
https://www.oaic.gov.au/privacy/australian-privacy-principles
Specifically, APP 1.1 mandates that healthcare providers implement effective measures to protect patient data from unauthorized access, modification, or disclosure. This translates to robust security controls that safeguard electronic health records (EHRs) and other sensitive information.
The ramifications of failing to secure patient data can be severe. A data breach not only undermines patient trust but also exposes healthcare providers to significant legal and financial repercussions. The OAIC has the authority to issue substantial fines for non-compliance with the APPs. Furthermore, data breaches can result in costly litigation and reputational damage, potentially leading to a decline in patient confidence and referrals.
The Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) emphasizes the importance of proactive data security measures for healthcare organizations. By prioritizing patient data security and actively mitigating cyber risks, Australian healthcare providers can fulfill their legal and ethical obligations while fostering a climate of trust with their patients.
What is an IAM Assessment?

In the intricate world of healthcare data security, Identity and Access Management (IAM) acts as a digital gatekeeper. IAM establishes a framework for governing who can access patient data, what information they can view, and for what authorized purposes. This system ensures that only the right individuals have the necessary access to perform their duties efficiently, while simultaneously preventing unauthorized access attempts.
An IAM assessment serves as a comprehensive evaluation of an organization’s IAM practices in relation to safeguarding patient data. This in-depth analysis aims to identify potential vulnerabilities in access controls, misconfigurations in user permissions, and any gaps in compliance with relevant regulations such as the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs). By uncovering these weaknesses, healthcare providers can prioritize necessary improvements and strengthen their overall data security posture.
The scope of an IAM assessment for healthcare providers is typically multifaceted. It often involves reviewing access control policies and procedures, analyzing user access logs to identify anomalies, and evaluating the effectiveness of existing security measures in place to protect sensitive patient information. The assessment may also delve into user provisioning practices, password management protocols, and the overall architecture of the IAM system. Through this comprehensive examination, healthcare organizations gain valuable insights into their data security posture and can implement targeted measures to mitigate cyber risks and ensure patient data remains secure.
Benefits of Conducting an IAM Assessment

For Australian healthcare organizations navigating the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape, an IAM assessment offers a multitude of advantages:
- Enhanced Data Security Posture: By pinpointing weaknesses in access controls and user permissions, IAM assessments empower healthcare providers to fortify their data security defenses. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive patient information.
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: IAM assessments act as a pre-emptive measure, helping healthcare organizations identify and address vulnerabilities before they are exploited by cybercriminals. This significantly reduces the likelihood of costly and damaging data breaches.
- Streamlined Compliance with Regulations: Australian healthcare providers are subject to stringent data privacy regulations like the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs). An IAM assessment ensures alignment with these regulations by verifying that access controls and data security practices meet compliance requirements.
- Improved User Experience: Efficient access control systems are not just about security; they also enhance user experience. Through IAM assessments, healthcare organizations can optimize access permissions, ensuring authorized personnel have the necessary access to perform their duties efficiently while minimizing unnecessary hurdles.
- Cost Savings Through Optimized Access Controls: Inefficient access controls can lead to wasted resources and unnecessary administrative burdens. IAM assessments help identify areas for improvement, allowing healthcare organizations to optimize access controls and streamline workflows, potentially leading to cost savings in the long run.
By reaping these benefits, Australian healthcare providers can not only safeguard sensitive patient information but also foster a culture of trust and transparency within their organization.
The IAM Assessment Process
Conducting a successful IAM assessment for Australian healthcare providers is a methodical process typically involving several key stages:
1. Planning and Scoping
The foundation of a productive IAM assessment lies in meticulous planning and scoping. This initial phase involves clearly defining the assessment’s objectives. For instance, the assessment might focus on evaluating compliance with the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs), identifying vulnerabilities in access controls for electronic health records (EHRs), or assessing the effectiveness of user access provisioning practices.
Next, it’s crucial to identify key stakeholders within the healthcare organization. This may include personnel from IT security, data privacy, healthcare operations, and relevant clinical departments. Involving these stakeholders from the outset fosters a collaborative environment and ensures the assessment addresses the organization’s specific needs.
2. Data Collection and Analysis
Once the objectives and stakeholders are defined, the assessment team embarks on a comprehensive data collection and analysis phase. This stage involves reviewing various documents and artifacts critical to understanding the organization’s IAM practices. Examples include:
- Access control policies and procedures: These documents outline the organization’s approach to granting and managing user access to patient data.
- User access logs: Analyzing these logs can reveal patterns of access activity and identify any anomalies that might suggest unauthorized access attempts.
- System configurations: Evaluating the security settings of IT systems used to store and access patient data is vital for pinpointing potential weaknesses.
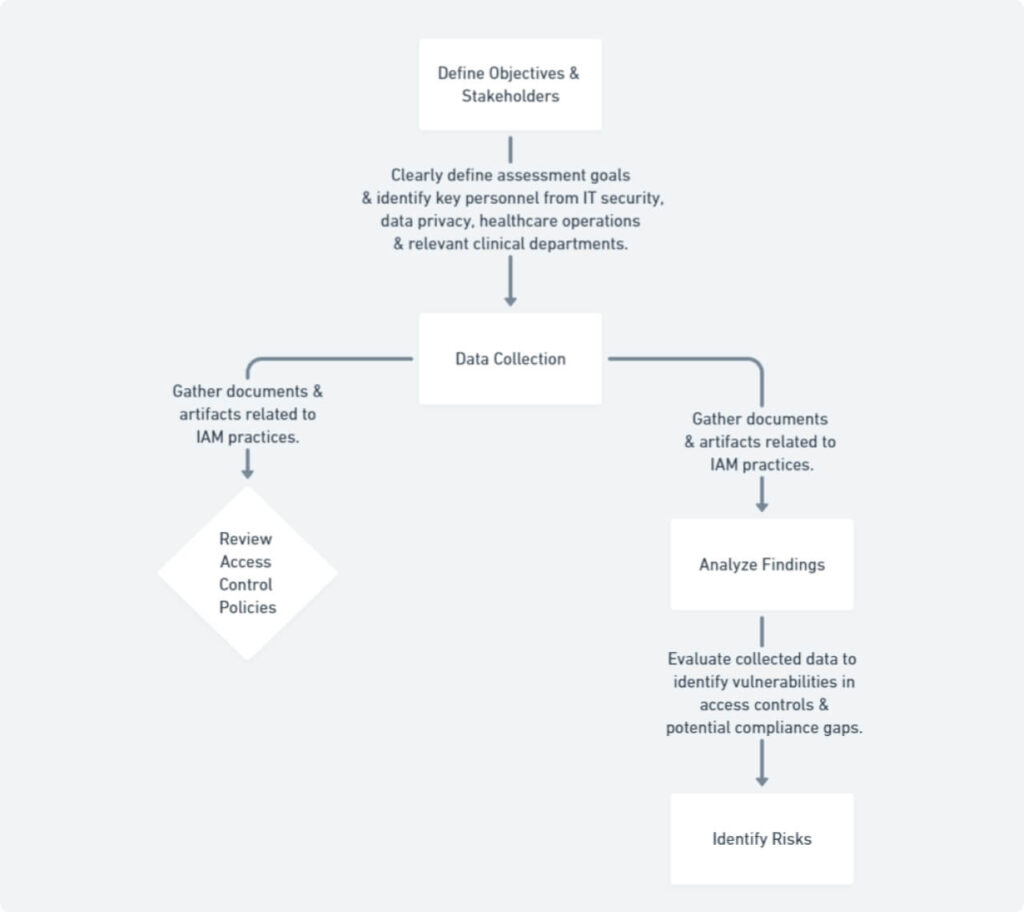
3. Risk Identification
Armed with the data collected, the assessment team can delve into risk identification. This stage involves analyzing the findings from the data collection phase to pinpoint vulnerabilities in the organization’s IAM practices. These vulnerabilities might include:
- Overly permissive user access permissions, granting individuals access to patient data beyond their job requirements.
- Weak password policies, making it easier for cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access.
- Outdated or unsupported access control software, creating security gaps.
By identifying these vulnerabilities, the healthcare organization can prioritize remediation efforts and strengthen their overall data security posture.
4. Reporting and Recommendations
The culmination of the IAM assessment is the creation of a comprehensive report outlining the findings and recommendations. This report should clearly articulate the identified vulnerabilities in access controls, potential compliance gaps, and the overall risk posture of the healthcare organization. More importantly, the report should provide actionable recommendations for improvement, such as revising access control policies, implementing multi-factor authentication or upgrading outdated security software.
5. Importance of Stakeholder Involvement
Throughout the entire IAM assessment process, maintaining open communication and collaboration with key stakeholders is paramount. Their involvement ensures the assessment addresses the organization’s specific needs and fosters buy-in for implementing the recommended improvements.
Preparing for an IAM Assessment

Undergoing an IAM assessment can be a smooth and productive experience for Australian healthcare providers with a little preparation. Here are some key steps to ensure a successful assessment:
1. Gather Relevant Documentation
The assessment team will rely heavily on reviewing existing documentation to gain a clear understanding of your organization’s IAM practices. Proactively gather and readily accessible documents like:
- Security policies: This includes policies governing access control, password management, and data security practices.
- Access control procedures: These documents outline the process for granting, reviewing, and revoking user access to patient data.
- User access logs: Having historical access logs readily available allows the assessment team to analyze access patterns and identify potential anomalies.
- System configuration documentation: This documentation details the security settings implemented on systems used to store and access patient data.
By compiling these documents beforehand, you can streamline the assessment process and ensure the team has the necessary information to conduct a comprehensive evaluation.
2. Identify Key Personnel
The assessment will likely involve interviews and discussions with various personnel within your organization. Proactively identify key individuals who can provide valuable insights into your IAM practices. These might include:
- IT security personnel responsible for access control management.
- Data privacy officers familiar with relevant regulations like the APPs.
- Staff from healthcare operations departments involved in user provisioning and access requests.
- Relevant clinical department representatives who can speak to their specific data access needs.
Having these key stakeholders readily available for communication with the assessment team fosters a collaborative environment and ensures a thorough evaluation.
3. Ensure Clear Communication and Cooperation
Open communication and cooperation are critical throughout the entire IAM assessment process. Clearly define points of contact within your organization who can liaise with the assessment team and address any questions or concerns that may arise.
By fostering a transparent and collaborative environment, Australian healthcare providers can ensure a smooth assessment experience and gain valuable insights into strengthening their data security posture.
Key Considerations for Australian Healthcare

Conducting IAM assessments in the Australian healthcare landscape necessitates a nuanced approach that balances stringent data privacy regulations with the need for efficient healthcare delivery.
A crucial consideration is ensuring alignment with the Australian Privacy Principles (APPs) enshrined in the Privacy Act 1988 (Cth). These principles govern the collection, use, disclosure, and storage of personal information, including sensitive patient data. An IAM assessment specifically tailored to the healthcare context should evaluate access controls against these principles. For instance, the assessment should verify that access to patient data is limited to authorized personnel with a legitimate need to know, adhering to APP 1.3.
However, robust data security shouldn’t impede the ability of healthcare professionals to access patient information promptly. The IAM assessment process should consider the workflows and access requirements of various clinical departments. Finding the optimal balance between security and efficiency is paramount. This might involve implementing role-based access controls that grant appropriate access levels to different healthcare professionals based on their specific roles.
Australian healthcare organizations can leverage IAM assessments to strike this critical balance. By identifying vulnerabilities in access controls and ensuring compliance with the APPs, healthcare providers can safeguard sensitive patient data while simultaneously optimizing access for authorized personnel, ultimately fostering a secure and efficient healthcare environment.
In the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape, Australian healthcare providers entrusted with safeguarding sensitive patient data require robust defenses. IAM assessments serve as a powerful tool for identifying vulnerabilities in access controls, bolstering compliance with data privacy regulations and ultimately minimizing the risk of data breaches. By implementing regular IAM assessments, healthcare organizations can proactively fortify their data security posture, foster patient trust and ensure the continued delivery of high-quality healthcare.
